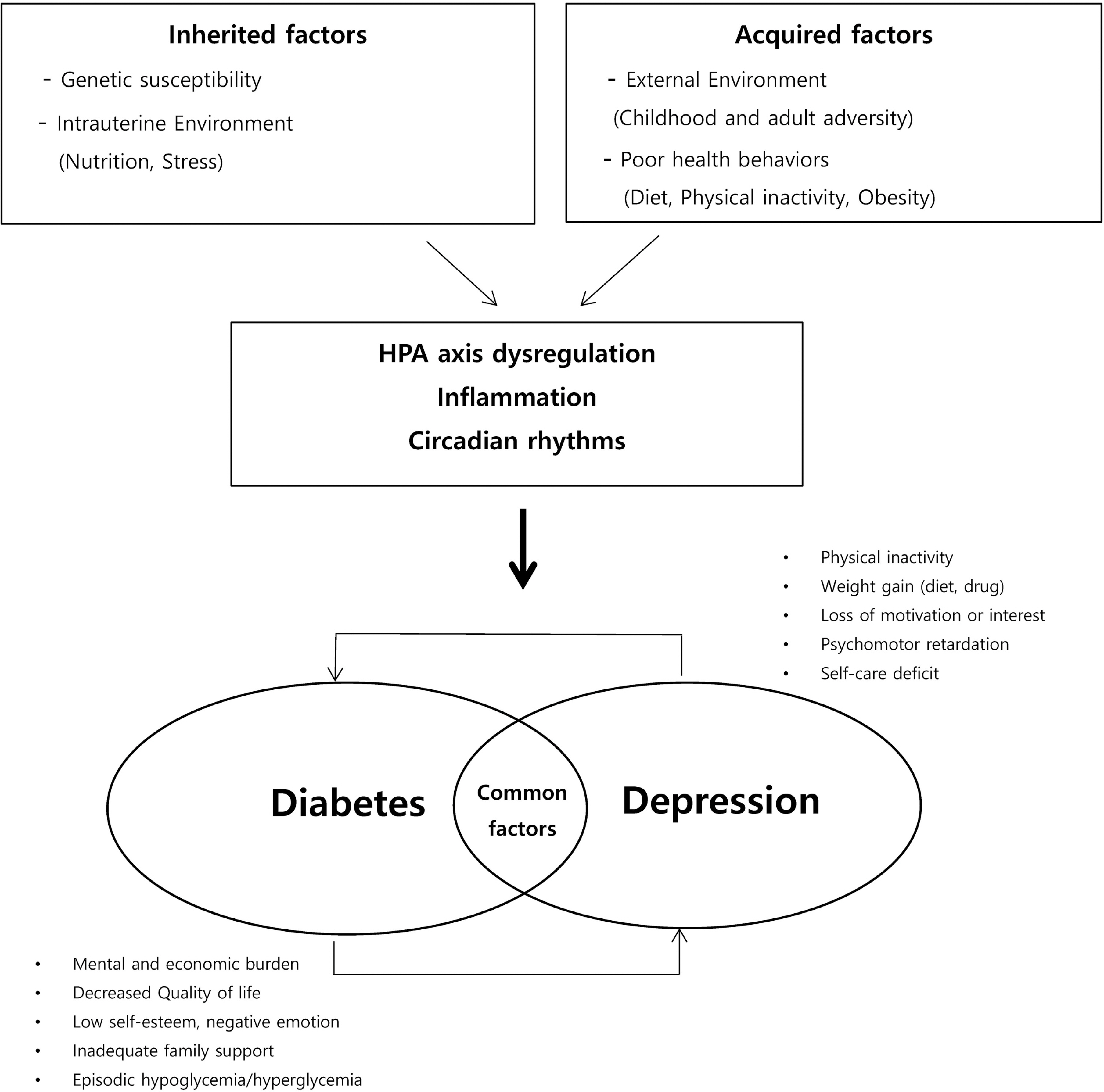
2.USV Pharmaceutical CorporationDiabetes: a medical od-yssey. Tuckaho: USV Pharmaceutical Corporation; 1971.
3.Korean Diabetes AssociationDiabetes. 5th ed.Seoul: Panmuneducation; 2018.
5.Dejgaard A, Gade A, Larsson H, Balle V, Parving A, Parving HH. Evidence for diabetic encephalopathy. Diabet Med 1991;8:162-7.


6.Jesulola E, Micalos P, Baguley IJ. Understanding the pathophysiology of depression: from monoamines to the neurogenesis hypothesis model - are we there yet? Behav Brain Res 2018;341:79-90.


7.Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ. The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2001;24:1069-78.

10.Tab├Īk AG, Akbaraly TN, Batty GD, Kivim├żki M. Depression and type 2 diabetes: a causal association? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014;2:236-45.


13.Korean Neuropsychiatric AssociationTextbook of neuro-psychiatry. 3rd ed.Seoul: iMiS company; 2017.
14.American Psychiatric Association eds. DSM-5. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed.In: Kwon JS, Kim JJ, Namgung G, Park WM, Shin MS, Yoo BH, , Seoul: Hakjisa; 2015. c2013..
16.Park HS, Hong YS, Lee HJ, Ha EH, Sung YA. The association between depressive symptoms and glycemic control in the patients with diabetes mellitus. Korean J Med 2003;64:204-11.
17.Lin EH, Rutter CM, Katon W, Heckbert SR, Ciechanows-ki P, Oliver MM, et al. Depression and advanced complications of diabetes: a prospective cohort study. Diabetes Care 2010;33:264-9.

18.Zhang X, Norris SL, Gregg EW, Cheng YJ, Beckles G, Kahn HS. Depressive symptoms and mortality among persons with and without diabetes. Am J Epidemiol 2005;161:652-60.